Understanding Employee Provident Fund (EPF) Form 6A: An Overview

EPF Form 6A
It is a crucial document for employers in India who manage Employee Provident Fund (EPF) contributions for their employees. This form plays an essential role in the annual reporting of provident fund contributions made by both employers and employees. Below is a comprehensive overview of EPF Form 6A, including its purpose, the information it contains, and the process for filing it.
What is EPF Form 6A?
EPF Form 6A, also known as the Annual Contribution Statement, is a summary form that employers are required to submit to the Employees’ Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO) at the end of each financial year. The form details the total contributions made by both the employer and the employees to the EPF during the year.
Purpose of EPF Form 6A
The primary purpose of EPF Form 6A is to provide a consolidated statement of all monthly contributions reported through Form 12A throughout the year. This helps the EPFO maintain accurate records of each employee’s provident fund contributions and ensures that employers comply with statutory obligations.
Contents of EPF Form 6A
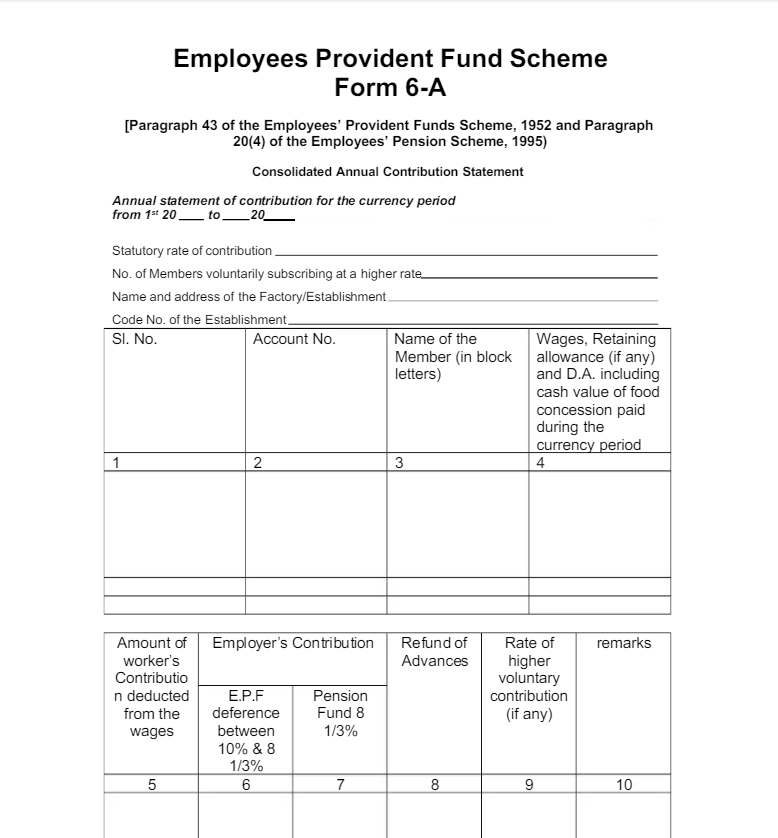
EPF Form 6A includes several key details:
- Employer Information:
- Name and address of the establishment.
- EPF code number of the establishment.
- Employee Information:
- Provident Fund Account Number (PF Account Number) for each employee.
- Employee’s full name as recorded in the EPF system.
- Contribution Details:
- Total amount of contributions made by the employee during the financial year.
- Total amount of contributions made by the employer during the financial year.
- Portion of the employer’s contribution that is allocated to the Employee Pension Scheme (EPS).
- Wage Details:
- Details of wages, including basic wages, dearness allowance, and any retaining allowance, for each month.
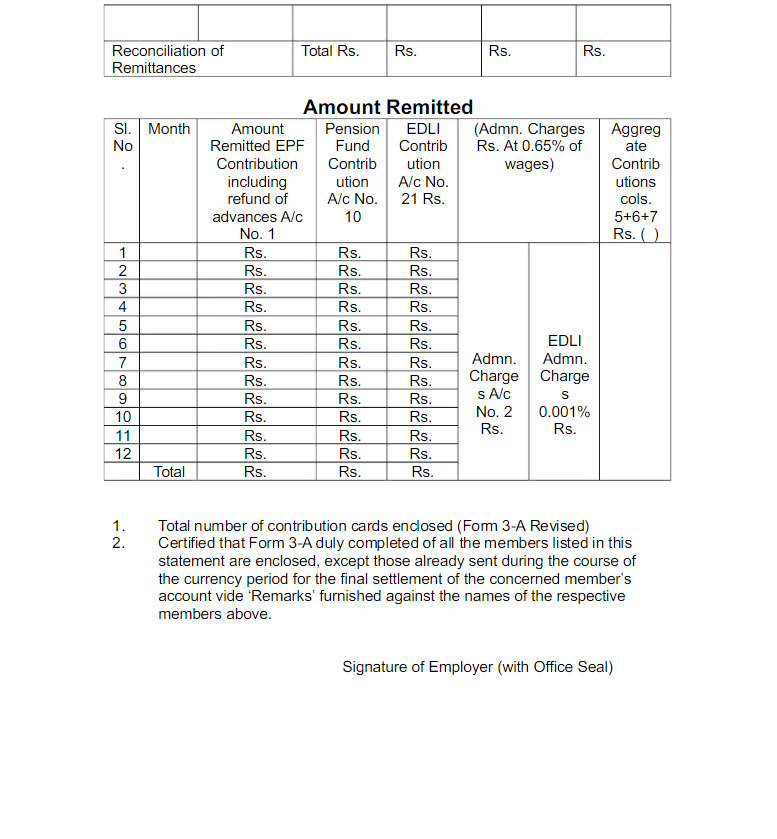
- Total Contributions:
- A summary of the total contributions for each employee, including both employee and employer contributions as well as pension contributions.
Filing Procedure for EPF Form 6A
Preparation:
- The employer must prepare Form 6A at the end of the financial year by compiling data from the monthly returns filed using Form 12A. It should include all contributions made during the year.
Verification:
- Before submitting, the employer should verify all details, including the accuracy of employee information, contribution amounts, and PF account numbers.
Submission:
- The form must be submitted to the EPFO by the end of April of the following financial year. Employers can submit the form either manually or through the EPFO’s online portal.
Acknowledgment:
- Upon submission, the EPFO provides an acknowledgment, confirming the receipt of the form.
Importance of EPF Form 6A
Legal Compliance: Submitting Form 6A is a legal requirement under the EPF Act. Non-compliance can lead to penalties and legal action against the employer.
Record Keeping: Form 6A serves as an official record of all contributions made during the year, which is vital for both employers and employees.
Transparency: It ensures transparency in the management of employees’ provident fund accounts by providing a clear summary of contributions.
Consequences of Non-Submission or Incorrect Filing
Failure to submit EPF Form 6A or submitting incorrect details can result in penalties for the employer. It can also cause discrepancies in employee records, leading to issues in the future, such as delays in claims or incorrect pension calculations.
This is how Form-6A looks like:-
Conclusion
EPF Form 6A is a vital document that ensures the proper management and recording of provident fund contributions in India. Employers must take care to prepare and submit this form accurately and on time, as it not only fulfills legal obligations but also safeguards the financial interests of their employees. By understanding the importance and procedure for filing EPF Form 6A, employers can ensure compliance with EPF regulations and contribute positively to the financial security of their workforce.
Frequently Asked Questions
A: EPF Form 6A is an annual contribution statement that employers must submit to the Employees’ Provident Fund Organization (EPFO). It summarizes the total contributions made by both the employer and employees to the EPF for the entire financial year. This form is crucial for maintaining accurate records and ensuring compliance with EPF regulations.
A: Employers are required to submit EPF Form 6A at the end of each financial year. The form must be submitted by the end of April of the following financial year, summarizing the contributions made during the preceding year.
A: EPF Form 6A includes detailed information such as the employer’s name and code, the names and PF account numbers of all employees, and the total amount of contributions made by both the employer and employees during the year. It also contains details about the pension contributions under the Employees’ Pension Scheme (EPS).
A: While Form 12A is a monthly statement that provides details of EPF contributions for a specific month, Form 6A is an annual summary of all the contributions made throughout the financial year. Form 6A consolidates the information reported in Form 12A for each month.
A: Failure to submit EPF Form 6A on time can lead to penalties and legal consequences for the employer. Additionally, it can result in discrepancies in the employees’ EPF accounts, potentially causing issues with future claims or pension calculations. Therefore, timely and accurate submission is critical.
About The Author

Gagan Gupta
Founder & CEO
Gagan Gupta is a distinguished authority in the realm of accounting and tax compliance. With extensive expertise in managing comprehensive tax compliance procedures—ranging from income tax and GST to TDS and TCS filings across various industries—Gagan has established himself as a pivotal figure in the field. His proficiency extends to meticulously teaching the intricacies of the filing process, elucidating even the most minute details, and identifying common errors along with their resolutions.
Gagan Gupta’s profound understanding of every facet of taxation and accounting enables him to share invaluable insights through industry-specific blogs. These blogs serve as a rich resource for fellow industry professionals, including advocates and Chartered Accountants (CAs). By imparting his extensive knowledge and practical experience, Gagan Gupta not only enriches his readers but also contributes significantly to the broader discourse in the taxation and finance community.










